The Global Market, According to Your Time Zone
A study published on Slate highlights differences between standard and solar time around the world. Businesses operating across multiple countries know they need to account for changes in timezone, but this study explores how the rhythms of the sun affect the international workday and why they should influence modern business models.
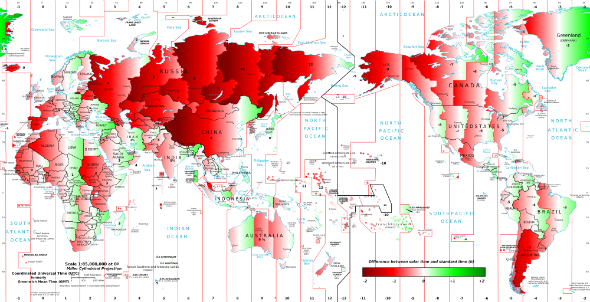
The map by Google engineer Stefano Maggiolo, published for Slate, contains an international business lesson.
The geographical data visualization represents differences around the globe between time as read on a clock and “solar time,” a schedule that puts the sun directly overhead at exactly noon. The places where the sun arrives ahead of the solar schedule are marked in green, while places where the sun comes “late” are shown in red. The color deepens the more standard designated time in the specific location deviates from solar time.
The accompanying Slate article, “How Wrong Is Your Time Zone?”, detailed where the differences are most extreme, from provinces in Western China where the sun rises so late in the clock day that residents observe their own time in defiance of the government, to eastern parts of India where the sun comes up as early as 4:30 a.m. The Washington, DC-based author notes how his local clock time is not so
far off solar time and concludes by quipping that Spain’s “siestas and 10 p.m. dinners probably won’t be coming to [the US] capital anytime soon.”
It’s true that the majority of countries live according to standard time, but the solar reality on display lends insight into legitimate cultural differences. Each region conceives differently of the day according to how clock time relates to the sun. The Spanish may be playfully singled out for siestas, but Spain’s alternative workday provides an illustration of how this varying cultural relationship to time can impact business practices.
The logistical and cultural implications of solar time have particular importance for businesses operating around the world.
International Markets Re-conceived
In the global marketplace, solar and standard designated time differences can greatly affect businesses’ long-range operations and productivity. It can be difficult to facilitate seamless transactions between timezones from a logistical standpoint, and the recent study of solar time highlights how it may also be challenging to coordinate business practices across cultures.
Variations in the global schedule and the resulting attitudes encourage businesses to choose between two general models: operating in a localized market or creating an automated system to handle the diverse international market.
On a large scale, whether a business chooses one kind of market or the other depends on the traditions of the home country, whether they have access to technology and the state of the economy. From business to business, the choice between markets presents differently across industries.
In the food industry, for example, a small restaurant might naturally choose to operate in a localized market, sourcing food from local providers. When service does not rely on imported goods, other timezones do not have to factor into the business model. Regional businesses are free to tailor their products to the solar rhythm of the day and the cultural practices of local customers. Local trade stays in line with nature, serving the immediate community.
For internationally-oriented industries like finance and fashion, however, coordinating time zones comprises a crucial part of everyday operations. These are the industries that opt for machine-dominated systems that negate any timezone discrepancies.
Solar Time Sheds Light on Knowing Your Market
In the New York Times article “Tips for Increasing Sales in International Markets,” author Ian Mount emphasizes how important it is for small businesses to evaluate a product’s potential success before expanding into international markets.

Photo by Anna Shvets from Pexels
Solar time engages traditional concerns about accounting for changing timezones, but also raises questions about which regional cultures offer your business the best potential partners, specifically with regard to their relationship to time. Consider whether a given business culture values punctuality and mass efficiency versus building trust and developing intimate business relationships over time. If your new international partner wants to operate at a different pace or during different hours, your business may face unexpected compromises balancing desired production methods with stable relationships.
In today’s globalized economy, the informed businessperson can conceive of his market in the broadest possible sense, but maybe the biggest advantage of access to the globe is the ability to tailor the product to the market and the market to the product. For example, businesses can weigh the pros and cons of importing or exporting overseas. Maybe one culture presents the perfect partner while the product would be most likely to succeed in yet another market.
Small business owners, in particular, can ask themselves “Across what timezones and cultures will my operations and product be most efficient and successful?“ to design the most culturally sensitive and foolproof business plan. Once companies determine their international partners and audiences, then is the moment to consider learning the native languages of new colleagues. If you’re looking to smoothly integrate operations with foreign parties, consider contacting Language Trainers.
And if you need to train your employees so they can communicate with partners from other countries, explore our face-to-face and online language courses, tailored specifically to your business’ needs.